Dealing with pigmentation issues can be frustrating, especially in Malaysia’s tropical climate, where constant exposure to the sun’s intense rays can exacerbate dark spots and uneven skin tone. Whether it’s those stubborn sunspots or the remnants of an acne breakout, pigmentation concerns are common among many of us. Understanding how pigmentation develops and knowing the practical steps to manage it can make a significant difference in achieving a clear, radiant complexion.
What Causes Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation, or hyperpigmentation, occurs when certain areas of the skin become darker than the surrounding skin. This happens due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour. Studies have shown that up to 80% of people experience some form of hyperpigmentation in their lifetime.
For some, it might be the sun. For others, it may be genetics. People with darker skin tones are more prone to hyperpigmentation because they have more active melanocytes, the cells responsible for melanin production. Hormonal fluctuations, skin injuries like popped pimples and inflammatory conditions can make skin pigmentation worse.
Sun Exposure
One of the most common causes of hyperpigmentation is prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun. UV rays stimulate melanin production as a natural defence mechanism, leading to sunspots or age spots.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly in women, can trigger melanin overproduction. Conditions like melasma are often linked to pregnancy, birth control pills, or hormone replacement therapy, leading to dark patches on the skin.
Inflammation
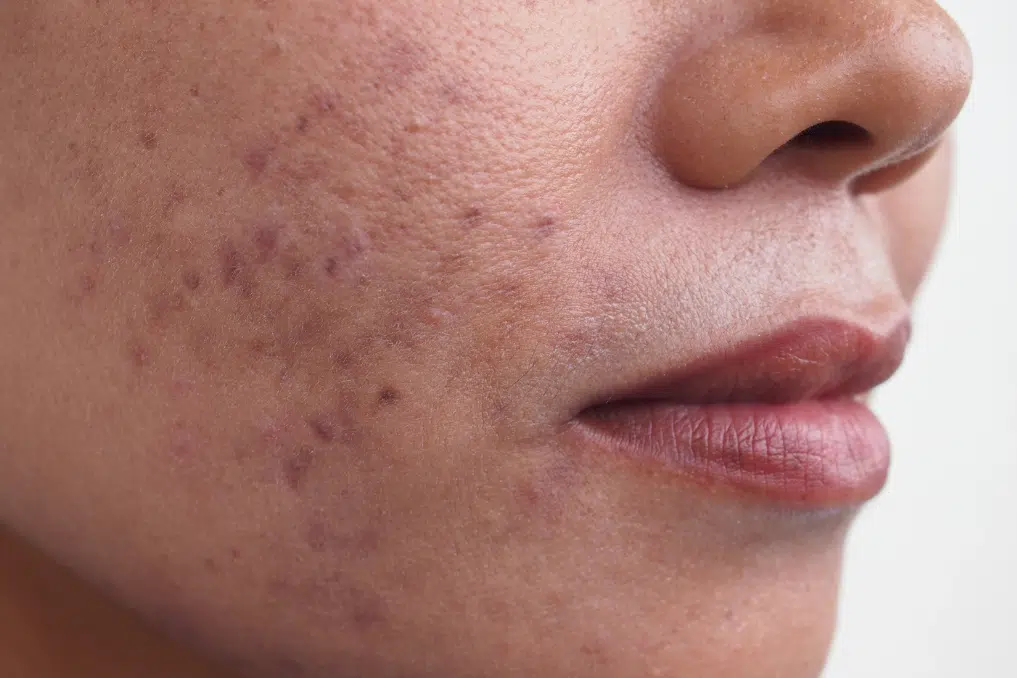
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) occurs following an injury or inflammation of the skin, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis. As the skin heals, it can leave behind darkened areas.
The Types of Hyperpigmentation

Hyperpigmentation can manifest in various forms, each with different characteristics and developed from the variety of causes listed in the previous section. You can identify the type of hyperpigmentation you have to find more effective solutions to address it.
- Sunspots (Solar Lentigines)
Sunspots, also known as age spots or liver spots, are flat, brown spots that appear on areas of the skin frequently exposed to the sun, such as the face, hands, shoulders, and arms. They result from prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, which increase melanin production in these areas. - Melasma
Melasma presents as larger patches of darkened skin, often on the face, particularly on the cheeks, forehead, nose, and upper lip. This type of hyperpigmentation is commonly linked to hormonal changes, such as those experienced during pregnancy, birth control use, or hormone replacement therapy. It is more prevalent in women and people with darker skin tones. - Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
PIH occurs after an injury or inflammation of the skin, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis. As the skin heals, it can produce excess melanin, leading to dark spots or patches. This type of hyperpigmentation can affect all skin types but is more common in individuals with darker skin tones. - Freckles (Ephelides)
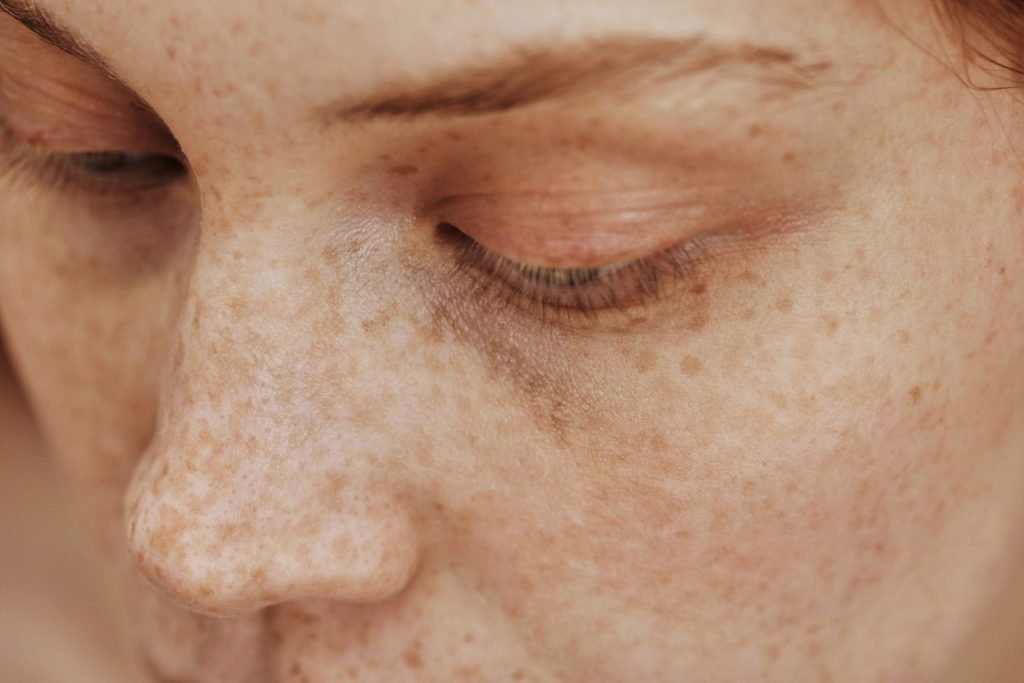
Freckles are small, brownish spots that usually appear on sun-exposed areas like the face, neck, and arms. They are genetic and become more prominent with sun exposure. Unlike other types of hyperpigmentation, freckles can fade during the winter months when sun exposure is reduced. - Dark Circles
Dark circles under the eyes can be a form of hyperpigmentation caused by a variety of factors, including genetics, lack of sleep, ageing, and sun exposure. They can also be exacerbated by the thinning of the skin under the eyes, making blood vessels more visible.
Preventive Measures for Skin Pigmentation
Protect Your Skin From the Sun
Everyone knows the number one rule to avoid skin pigmentation– stay out of the sun. Maintaining proper sun protection is paramount in preventing skin pigmentation, particularly in minimising the risk of dark spots and uneven skin tone caused by harmful UV rays.
Other than slathering yourself in SPF 50++ sunscreen on a hot day and taking a UV umbrella everywhere with you, incorporating Vitamin C into your skincare routine can help brighten the skin and prevent further pigmentation due to sun damage.
Keep Skin Moist to Boost Cell Turnover
Hydrated skin is more resilient to external factors that can trigger hyperpigmentation, making regular moisturising an essential preventive measure. By keeping your skin adequately hydrated, you create a protective barrier that reduces the risk of inflammation and dark spots. Moisturisers containing ingredients like glycerin and hyaluronic acid help maintain skin hydration, promoting healthy skin renewal and minimising the appearance of dark spots.
These ingredients work by attracting and retaining moisture in the skin, supporting cell turnover and overall skin health. Make moisturising a consistent part of your skincare routine to enhance cell regeneration and prevent pigmentation issues.
Don't Pick on Blackheads or Bug Bites
Avoid picking at blackheads or bug bites to prevent skin inflammation and post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Picking can lead to skin damage, causing melanocytes to overproduce melanin and result in dark spots. Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation often manifests as dark patches on the skin and can be challenging to treat.
By refraining from picking at your skin, you can reduce the risk of developing hyperpigmentation and promote overall skin health.
Effective Skincare for Hyperpigmentation

There are many ingredients that can help you address hyperpigmentation and an uneven skin tone. A Klinik also offers formulations made by our expert skin care professionals.
- Niacinamide is known to reduce hyperpigmentation and promote skin tone evenness.
- Retinol aids in accelerating skin cell turnover, gradually diminishing dark spots.
- Vitamin C products are effective in fading hyperpigmentation marks, leading to a more uniform complexion.
Additionally, consider incorporating microdermabrasion kits into your skincare routine to exfoliate dead skin cells, revealing a brighter and more radiant skin surface. Remember to perform a patch test before full application, and consistency is key to seeing visible improvements in skin pigmentation over time.
Hyperpigmentation Treatment Options
Topical Treatments
With a consultation, our doctors can give recommendations of the best ingredients to reduce your hyperpigmentation based on its probable cause. This can range from hydroquinone, common depigmenting agent that lightens dark spots by inhibiting melanin production; retinoids, Vitamin A derivatives such as tretinoin help to speed up cell turnover, promoting the shedding of pigmented skin cells; or Vitamin C, an antioxidant that can help to lighten hyperpigmentation by inhibiting melanin synthesis and protecting skin from further damage.
We recommend getting clinical grade products with clear percentages so you have a better idea of the strength of the ingredient and be able to adjust your skincare around it.
Chemical Peels
The same way you integrate acids like AHA and BHA into your skincare routine, chemical peels are the stronger, clinical version. Chemical peels involve applying a chemical solution to the skin, which exfoliates the top layers and encourages new skin growth.
It removes the outer layers of the skin, which contain dead cells and melanin. This process stimulates the growth of new, healthier skin cells and can significantly reduce the appearance of dark spots and uneven skin tone.
There are different types of chemical peels, ranging from superficial to deep.
Superficial peels use mild acids like alpha-hydroxy acids (AHAs) to gently exfoliate. They are ideal for mild hyperpigmentation and can be done regularly with minimal downtime.
Medium Peels use stronger acids like glycolic or trichloroacetic acid (TCA) to penetrate deeper layers of the skin. These are more effective for moderate hyperpigmentation and require more downtime.
Deep Peels use potent acids like phenol to reach the deeper layers of the skin. They are used for severe hyperpigmentation but require significant recovery time and have higher risks.
Microneedling
Microneedling involves using fine needles to create micro-injuries in the skin, stimulating collagen production and skin regeneration. The micro-injuries trigger the skin’s natural healing process, increasing collagen and elastin production. This helps in the turnover of pigmented skin cells and the growth of new, evenly toned skin.
The procedure involves a microneedling device is rolled or stamped across the skin. Additionally, microneedling is minimally invasive with relatively low downtime. It can improve skin texture, reduce pigmentation, and enhance the absorption of topical treatments.Several sessions are usually required, spaced a few weeks apart, to achieve optimal results.
Aesthetic Clinic in Penang
Get Rid of Hyperpigmentation at A Klinik Signature

At our clinic in Penang, we provide a wide range of services to address skin pigmentation concerns effectively. From chemical peels that exfoliate the skin and reduce pigmentation to laser therapies that target specific areas with precision, we’ve diverse treatment options available. Skilled doctors will evaluate your skin condition and recommend personalised treatment plans.








